Deoghar City of Jharkhand: A Great Historical and Cultural
Introduction
Deoghar, also known as the “Abode of Gods,” is one of the most prominent cultural, religious, and historical cities of Jharkhand, India. Situated in the northeastern part of the state, Deoghar holds immense importance because of its sacred temples, spiritual atmosphere, ancient history, and vibrant traditions. The city is particularly famous for the Baidyanath Jyotirlinga Temple, one of the twelve Jyotirlingas of Lord Shiva, making it one of the holiest pilgrim centers for Hindus.
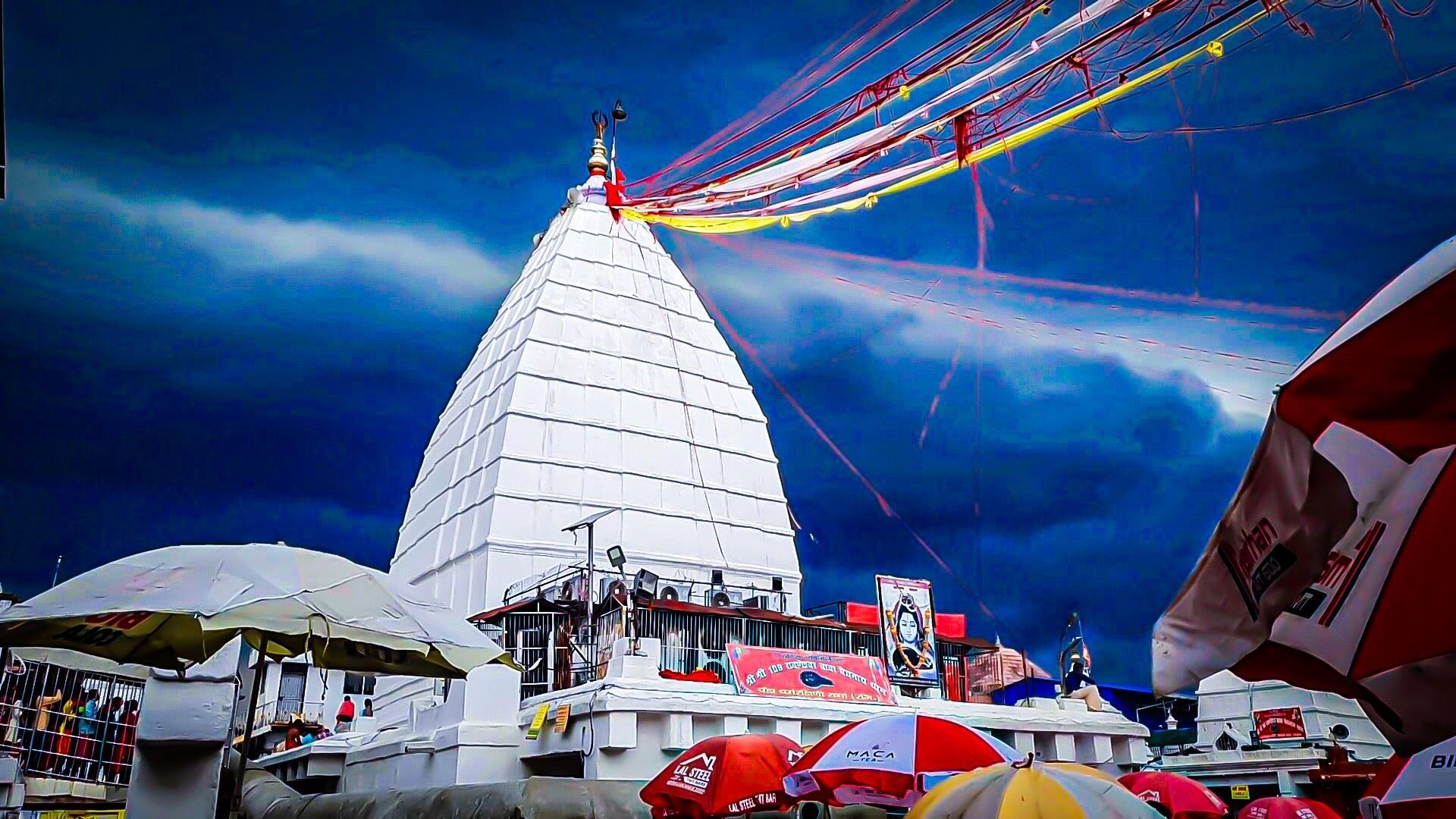

However, Deoghar’s story is not just about religion—it is also about its ancient history, tribal heritage, cultural evolution, Mughal connections, British rule, and modern development. This article takes you through the 1600 years of rich history of Deoghar city and how it grew into the spiritual and cultural heart of Jharkhand.
Early History of Deoghar
The origins of Deoghar trace back to ancient India, when it was a center of tribal settlements and nature worship. The Santhal and Paharia tribes lived in this region, worshipping forests, rivers, and hills as sacred entities. Deoghar’s name itself comes from Sanskrit—“Deo” (God) and “Ghar” (home), meaning the “Home of Gods.”
Archaeological evidence and ancient texts suggest that the region was known for Shaivism (worship of Lord Shiva) since the early centuries. The Baidyanath temple complex, believed to be several centuries old, was built on the foundations of much older shrines.
Mythological Connection
According to Hindu mythology, Deoghar is linked to the story of Ravana, the king of Lanka. Legend says that Ravana worshipped Lord Shiva and carried the Shivlinga from Mount Kailash to Lanka. On his way, he stopped at Deoghar to rest. However, due to divine intervention, the Shivlinga was placed permanently at Deoghar, making it one of the twelve Jyotirlingas. This legend has given Deoghar eternal importance in Hindu religious history.
Medieval History of Deoghar
During the medieval period, Deoghar became a hub for pilgrimage and temple culture. Kings and rulers from neighboring regions contributed to the development of temples, mathas (monasteries), and religious schools.
Influence of Regional Kingdoms
- The region was under the rule of the Nagvanshi dynasty and later came under the influence of Bengal and Bihar kingdoms.
- Many temples and shrines were constructed during this period, which still stand as examples of medieval Indian temple architecture.
- Deoghar also became a place of cultural exchanges, where Brahmins, monks, and saints gathered to spread Shaivism, Vaishnavism, and Tantric practices.
Mughal Era
During the Mughal rule, Deoghar came under the subah of Bengal. The Mughal emperors allowed the continuation of Hindu pilgrimages but imposed taxes. Despite this, the Baidyanath Dham continued to flourish as thousands of pilgrims visited annually. The temple became not only a spiritual hub but also a center of trade and economy, as fairs and markets developed around the pilgrim gatherings.
Deoghar During British Rule
With the arrival of the British East India Company in the 18th century, Deoghar saw significant changes.
Colonial Influence
- In 1765, when the British gained control over Bengal, Bihar, and Odisha after the Treaty of Allahabad, Deoghar came under their administration.
- The British established roads, railways, and postal services, which helped pilgrims and traders travel more easily to Deoghar.
- However, the tribal communities of the Santhal and Paharia strongly resisted British rule. The Santhal Rebellion (1855–56) had a major impact on Deoghar’s surrounding areas.
Religious Growth
- The British recognized the importance of Baidyanath Temple as it attracted lakhs of pilgrims. They introduced some administrative systems to regulate fairs, pilgrimages, and temple revenues.
- Shrawan Mela (a month-long pilgrimage during July-August) gained greater prominence during this period, as railways helped connect Deoghar with other parts of India.
Modern History of Deoghar
In the 20th century, Deoghar witnessed both religious revival and educational growth.
Role in Freedom Struggle
- The people of Deoghar actively participated in the Indian independence movement.
- Local leaders and youth supported the Quit India Movement (1942) and other nationalist campaigns.
- The area was also a safe retreat for many leaders who used Deoghar’s spiritual atmosphere to strategize and rejuvenate.
Post-Independence Development
After India’s independence in 1947, Deoghar gradually became one of the fastest-growing towns in Bihar (before Jharkhand was carved out in 2000).
- New schools, hospitals, and railway connections were built.
- In 2000, when Jharkhand was formed, Deoghar was officially recognized as one of its key religious and cultural cities.
- In 2022, the government inaugurated Deoghar Airport, boosting its connectivity and tourism.
Cultural and Religious Importance of Deoghar
History of Deoghar is deeply tied with its religious significance. The city is often called “Baba Baidyanath Dham” after its famous temple.
Baidyanath Jyotirlinga Temple
- One of the 12 Jyotirlingas in India.
- The temple complex consists of 22 temples dedicated to Shiva and other deities.
- The shrine attracts millions of devotees every year, especially during Shrawan month, when pilgrims known as Kanwariyas carry holy Ganga water from Sultanganj to offer at the temple.
Other Temples and Spiritual Sites
- Naulakha Temple – built by the queen of Pathuria Ghat, similar in style to the Ramakrishna Temple in Belur Math.
- Tapovan Hills – believed to be the meditation site of Lord Shiva.
- Basukinath Temple – another prominent Shiva temple connected with Baidyanath Dham traditions.
Educational and Cultural Growth
In the 20th and 21st centuries, Deoghar transformed from a purely religious town to a hub of education and culture.
- Establishment of Ramakrishna Mission Vidyapith (1922) – one of the oldest and most respected schools of eastern India.
- AIIMS Deoghar (2019) – a major medical institute serving Jharkhand and nearby states.
- Deoghar College and other institutions have contributed to the city’s growing reputation as a center of learning.
Modern Development and Tourism
Today, Deoghar stands as a perfect blend of spirituality and modernity.
- Deoghar Airport (2022) connects the city to Delhi, Kolkata, Patna, and Ranchi.
- Roads and hotels have been developed to cater to the massive inflow of tourists.
- Government has plans to make Deoghar a world-class religious tourism circuit under the Prasad Scheme.
Festivals and Fairs of Deoghar
Deoghar’s history is incomplete without mentioning its vibrant festivals:
- Shrawan Mela – Asia’s longest religious fair where lakhs of Kanwariyas visit.
- Durga Puja & Kali Puja – celebrated with grandeur, influenced by Bengal traditions.
- Tribal Festivals – Santhal and Paharia communities celebrate Sohrai, Karam, and Sarhul.
These festivals showcase the blending of tribal traditions with mainstream Hindu culture.
Timeline of Deoghar’s Historical Journey
| Period | Historical Significance |
|---|---|
| Ancient Era | Tribal settlements, Shaivism, Ravana legend of Baidyanath Jyotirlinga |
| Medieval Period | Rise of temples, Nagvanshi rule, Bengal influence, Mughal taxation |
| Mughal Era | Pilgrimage growth, temple economy flourished |
| British Era | Santhal Rebellion, temple regulation, railways increased pilgrim flow |
| 20th Century | Freedom struggle, Ramakrishna Mission Vidyapith, post-independence growth |
| 21st Century | Jharkhand formation (2000), AIIMS (2019), Deoghar Airport (2022) |
Conclusion
The history of Deoghar city in Jharkhand is a fascinating journey of faith, resilience, and cultural growth. From its tribal roots and mythological legends to medieval temples, Mughal encounters, British rule, and modern development, Deoghar has evolved into a unique blend of ancient spirituality and modern progress.
Today, it is not only a major religious destination but also a growing hub for education, healthcare, and tourism. The sacred city of Deoghar continues to uphold its title as the “Abode of Gods”, welcoming millions of pilgrims and travelers who seek both spiritual peace and cultural enrichment.

1 thought on “Deoghar City of Jharkhand: A Great Historical and Cultural”